
Diamond Guide
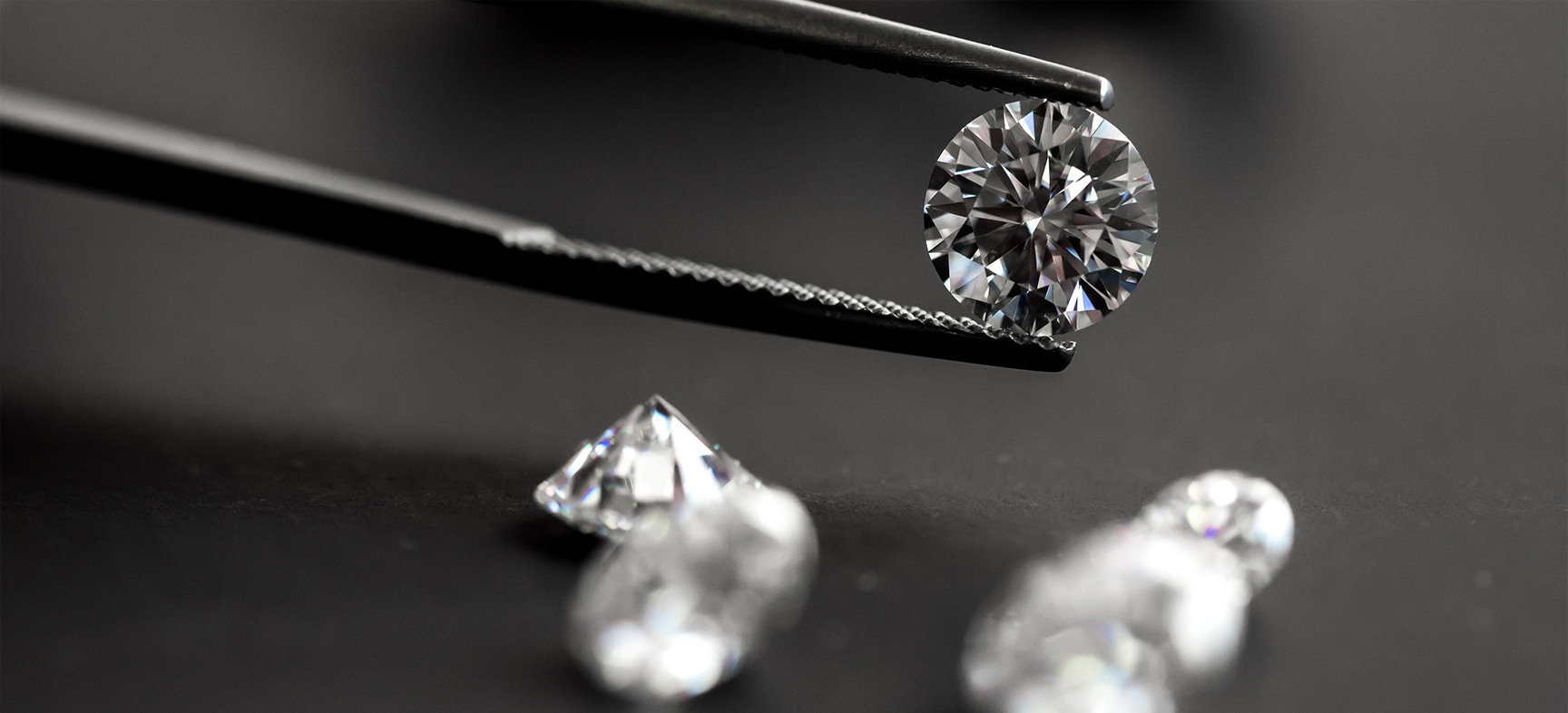
Picking the perfect diamond can be a mine field of information! Ultimately no matter the science the most important factor is what the stone means to you and what the piece represents. Whether it’s your first diamond in an engagement ring or a special pair of earrings for an anniversary, the diamonds will look as beautiful after 50 years as the day you received them.At Whittles we take great care to ensure all the diamonds we carry are of the finest quality, all you need to do is pick your perfect piece.
Cut
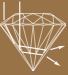
Diamond dimensions overly deep.
Lumination is lost through the sides.

Perfect dimensions.
All luminationis captured.
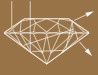
Shallow Diamond.
Lumination is lost.
Cut quality is the factor that fuels a diamond’s fire, sparkle and brilliance. The allure and beauty of a particular diamond depends more on cut quality than anything else. The GIA Diamond Cut Grading System for standard round brilliants in the D-to-Z colour range is based on the assessment of seven components.The first three — brightness (the total light reflected from a diamond), fire (the dispersion of light into the colours of the spectrum), and scintillation (the pattern of light and dark areas and the flashes of light, or sparkle, when a diamond is moved) — are appearance-based aspects. The remaining four — weight ratio, durability, polish, and symmetry — are related to a diamond's design and craftsmanship.

Brilliant Cut

Marquise Cut

Pear Cut

Oval Cut

Cussion Cut

Princess Cut
Colour
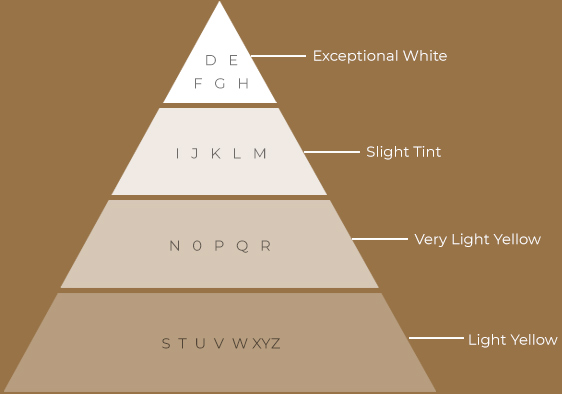
Diamond colour is all about what you can’t see. Diamonds are valued by how closely they approach colourlessness – the less colour, the higher their value. (The exception to this is fancy colour diamonds, such as pinks and blues, which lie outside this colour range.) GIA’s colour-grading scale for diamonds is the industry standard. The scale begins with the letter D, representing colourless, and continues with increasing presence of colour to the letter Z, or light yellow or brown. Each letter grade has a clearly defined range of colour appearance. Diamonds are colour-graded by comparing them to stones of known colour under controlled lighting and precise viewing conditions.
Clarity
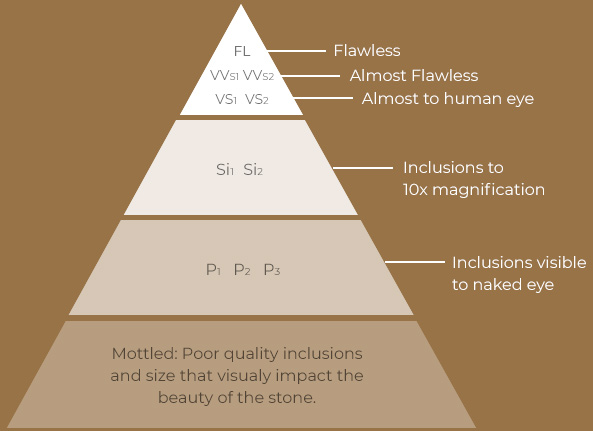
Diamonds are formed deep within the earth, under extreme heat and pressure. For this reason, they often contain unique birthmarks, either internal (inclusions) or external (blemishes). Diamond clarity refers to the absence of these inclusions and blemishes. Diamonds without these birthmarks are rare, and rarity affects a diamond’s value. Diamonds are assigned a clarity grade that ranges from flawless (FL) to diamonds with obvious inclusions (I3).
Carat
Diamonds are weighed in metric carats: one carat is equal to 0.2 grams and is the standard unit of weight for diamonds and other gemstones. The carat takes it's name from the carob seed. These seeds were used because they were small and had a fairly uniform weight. Early gem traders used them as counterweights in their balance scales.

2.00ct

1.50ct

1.00ct

0.50ct

0.20ct